Every time you flip a light switch, turn on the faucet, or connect to Wi-Fi, you’re relying on public utilities. These invisible systems electricity, water, gas, sewage, and telecommunications, keep society running. But behind every spark, every drop, every dial tone is a massive workforce making it all happen.
That leads to the big question how many jobs are available in public utilities? And more importantly, are these careers worth pursuing in 2025 and beyond?
Let’s unpack the career landscape, salaries, pros and cons, and where future growth lies.
What Are Public Utilities? (And Why They’ll Never Go Out Of Style)?
Public utilities are essential services that people literally cannot live without. They cover:
- Electricity & Energy (power plants, renewable energy, grid maintenance)
- Water Supply & Sanitation (treatment plants, plumbing, waste management)
- Natural Gas (distribution, safety, engineering)
- Telecommunications (fiber optics, broadband, data networks)
Because these are core to daily life, jobs in utilities stay in demand even during recessions.
How Many Jobs Are Available In Public Utilities?
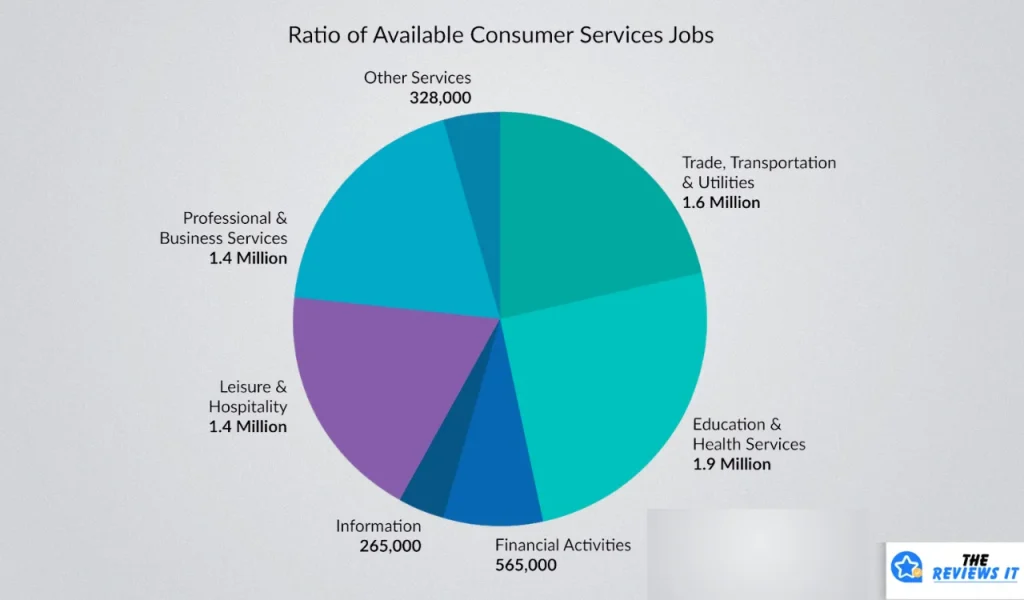
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics and industry reports, over 550,000 jobs are directly tied to public utilities in the U.S, with millions more indirectly connected through supply chains, contractors, and local services
So when people ask, How many jobs are available in public utilities? The answer is a lot, across a wide spectrum of roles. And with the rise of renewable energy and smart technology, that number is expected to grow steadily through 2030.
With this stability, workers can also focus on strengthening their personal finances and credit health platforms like Traceloans.com credit Score makes it easier to track and improve financial standing over time.
Learn How To Improve Your Financial Future with Traceloans Com Credit Score
Types Of Jobs In Public Utilities
Public utilities combine blue- and white-collar jobs, requiring diverse skills from fieldwork to planning. Here’s a look at key career categories:

1. Engineering Roles
Engineers are the backbone of the public utilities sector, designing, maintaining, and upgrading the infrastructure that powers everyday life. Some key positions include:
- Electrical Engineers: Work on power generation, transmission, and distribution systems, ensuring reliable electricity reaches homes, businesses, and industries.
- Civil Engineers: Build and maintain dams, pipelines, and water treatment plants, creating safe and efficient systems for water and waste management.
- Petroleum Engineers: Focus on natural gas and oil production, designing and overseeing drilling operations to extract energy safely and efficiently.
- Environmental Engineers: Handle sustainability projects like wastewater treatment, air quality monitoring, and renewable energy integration, helping utilities comply with environmental regulations.
2. Skilled Trades
Skilled trades are essential for keeping public utilities running daily, combining hands-on work, technical expertise, and problem-solving in the field. Key roles include:
- Linemen: Install and maintain electrical power lines, ensuring electricity reaches homes, businesses, and critical facilities safely. They often work outdoors in tough conditions, from storms to extreme heat or cold.
- Plumbers: Manage water supply and sewage systems, ensuring clean water flows and waste is safely handled, which is vital for public health.
- Electricians: Install, repair, and maintain electrical systems in utility plants, commercial buildings, and infrastructure, keeping operations safe and efficient.
- HVAC Technicians: Maintain heating, ventilation, and air conditioning systems, particularly in facilities like water treatment plants or utility offices, supporting both comfort and smooth operations.
3. Operations & Maintenance
These roles make sure utility systems run reliably and efficiently every day.
- Water Treatment Plant Operators: Oversee water treatment and distribution, ensuring safe, clean water for communities.
- Power Plant Operators: Manage power generation and monitor equipment to maintain a consistent electricity supply.
- Meter Readers: Track energy and water usage, while spotting potential issues or irregularities.
4. Management & Administrative Roles
These positions coordinate operations, staff, and projects to keep utilities functioning smoothly.
- Utility Managers: Supervise daily operations and guide teams to ensure efficient service delivery.Public
- Works Directors: Oversee municipal utilities, budgets, and infrastructure projects.
- Project Coordinators: Plan and track projects, making sure timelines and resources are on point.
5. Telecom & Tech
- These roles support modern infrastructure and communications, critical for smart utilities.
- Network Engineers: Design and maintain networks for monitoring and data management.
- Telecom Technicians: Install and repair communication systems for reliable service.
- Fiber Optic Installers: Install and maintain fiber optic cables for high-speed data and connectivity.
Education & Training Pathways
- Skilled trades usually require hands-on vocational programs or apprenticeships to gain practical field experience.
- Technical roles, such as electrical or civil engineers, generally need a college degree in the relevant field.
- Many utilities offer on-the-job training to help employees develop real-world skills and understand operational systems.
- Specialized certifications like water treatment, HVAC, or telecom licenses can significantly improve job prospects and career growth.
- Continuous learning and staying updated on evolving regulations and technology are essential for long-term success.
Impact Of Technology On Utility Careers
- Automation and AI are streamlining routine operations, reducing manual tasks but increasing the need for technically skilled employees.
- Smart grids, IoT, and remote monitoring systems require network and telecom experts to manage complex infrastructure.
- Renewable energy technologies, such as wind and solar, are creating new roles in installation, maintenance, and project management.
- Workers must stay adaptable, continually learning new skills to keep pace with technology-driven changes in the sector.
Similar automation trends are transforming other industries as well, as highlighted in the article on sales and automation.
Salary Insights: What You Can Expect
One of the reasons people ask how many jobs are available in public utilities is that salaries here are surprisingly strong.
Here’s your data in a proper table format:
| Role | Average Salary (U.S.) |
|---|---|
| Electrical Engineer | $100,000+ |
| Lineman | $74,000 |
| Plumber | $59,000 |
| Water Treatment Operator | $47,000 |
| Telecom Engineer | $81,000 |
| Public Works Director | $76,000 |
| Sanitation Worker | $38,000 (entry-level) |
Beyond steady salaries, many professionals also explore ways to grow their earnings outside their main job, using strategies like those shared on Money6x.com.
Learn How To Multiply Your Income Streams With Money6x.com
Future Trends: Where Are Utilities Headed?
The next decade will bring big changes in public utilities. Key trends include:
- Green Energy Surge: Wind and solar projects are growing 20%+, creating jobs in installation, maintenance, and engineering.
- Smart Grids & IoT: Demand for network and telecom experts is rising as utilities adopt smart, connected systems.
- Aging Workforce: Many older workers are retiring, opening opportunities for younger professionals.
- Urban Growth: Expanding cities need more water, waste, and energy systems, increasing demand for skilled workers.
Skills You Need To Succeed
If you want to build a career in public utilities, you’ll need a mix of technical and soft skills to handle the demands of the sector:
- Technical Skills: Knowledge in engineering, mechanics, and digital networks is essential to operate and maintain utility systems effectively.
- Problem-Solving: Quick thinking and decisive action are crucial during outages, emergencies, or unexpected system failures.
- Physical Fitness: Many field-based roles, such as linemen or technicians, require strength, endurance, and the ability to work in challenging conditions.
- Communication & Teamwork: Utilities rely on collaboration between engineers, technicians, operators, and managers to keep systems running smoothly.
- Adaptability: The sector is evolving rapidly with renewable energy, automation, and smart technologies, so being flexible and open to learning is key.
Alongside these streaming platforms, many users also turn to digital communities like Best Blogging Platform in 2025 to share reviews, discuss new shows, and explore trending entertainment blogs.
Quora Answers On Public Utility Jobs
On Quora, people often highlight that the public utilities sector is massive, offering over 2.6 million jobs in the U.S.These roles span electricity, water, gas, and key admin jobs that keep services running.
Many Quora answers also highlight how stable these jobs are, since services like power and water will always be in demand.
With infrastructure expanding and technology upgrading, the consensus on Quora is that public utilities offer steady careers with plenty of room for growth.
At the end of the day, when we ask how many jobs are available in public utilities, the bigger picture is this: these jobs aren’t just plentiful, they’re essential.
From keeping the lights on to bringing clean water into homes, public utility workers are the quiet backbone of modern life. And with technology, renewables, and urban growth, opportunities are only expanding.
So if you’re hunting for a career that’s stable, meaningful, and future-proof, public utilities might just be your power move.
FAQS
How many jobs are available in public utilities in 2025?
Over 550,000 in the U.S. alone, with steady growth projected.
Do public utility jobs require a college degree?
Not always. Skilled trades often require vocational training, while engineering and management roles need degrees.
Are these jobs safe from automation?
Some (like meter reading) are declining, but roles in renewable energy and network engineering are growing fast.
Which public utility job pays the most?
Petroleum engineers often earn $130K+.
Are public utilities a good career path?
Yes, if you value stability, benefits, and community impact.